Crossing the Deep Blue, Connecting to a Green Future
In the depths of the ocean lies an invisible energy artery, silently carrying clean energy from offshore wind farms, cross-sea islands, or international interconnected power grids to the mainland. This is TST CABLE’s high-voltage (HV) and ultra-high-voltage (EHV) submarine cable – a critical infrastructure for modern energy transformation, and a technological stronghold we have cultivated for over a decade.
Why are high-voltage and ultra-high-voltage submarine cables needed in the deep sea?
The underwater environment is far more challenging than imagined: thousands of meters of water pressure, high-salt corrosion, friction from seabed sediments, impact from fishing trawlers, ocean current erosion, and even the risk of earthquakes and landslides. Once laid, maintenance costs are high and the process is lengthy; “one-time success, thirty years of worry-free operation” is the only standard.
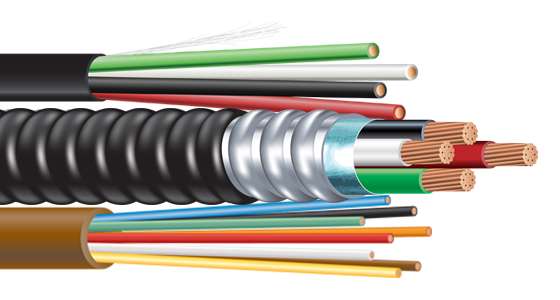
Therefore, our high-voltage and ultra-high-voltage submarine cable system is built with end-to-end reliability as its core:
Insulation Layer: Using ultra-clean cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) material, through multi-stage filtration and degassing processes, ensuring partial discharge <5 pC at 500kV;
Waterproof Barrier: Aluminum-plastic composite longitudinal wrapping + water-blocking tape + lead/copper alloy sheath, achieving complete longitudinal water blocking and preventing moisture diffusion;
Mechanical Protection: Double-layer galvanized steel wire armor (single/double armor optional), tensile strength exceeding 200 kN, resisting the most severe external forces on the seabed;
Intelligent Monitoring: Integrates distributed fiber optic temperature sensing (DTS) and carrier communication, providing real-time sensing of temperature, strain, and fault location for predictive maintenance.
Technological Strength, Proven in the Deep Sea
TST CABLE’s products cover voltage levels from 110kV to 500kV+, complying with international standards such as IEC 62893, CIGRE TB 490, and IEEE 1584, and are certified by classification societies such as BV, ABS, DNV, LR, and CCS. Successfully applied in:
✅ Asia’s first 500kV three-core submarine cable project
✅ Large-scale offshore wind power grid connection project in the North Sea
✅ Cross-strait island interconnected power transmission system
application
This submarine cable is used to transmit power to coastal islands, oil platforms, or cross rivers and lakes. The cable design is based on domestic or international standards such as VDE, IEC, and ICEA, or according to customer specifications.
Design and standards.
structure
Conductor: Copper conductor, water-resistant.
Conductor shielding: Extruded semiconducting material.
Insulation: XLPE.
Insulating shield: Extruded semi-conductive material.
Separator: Expansion zone.
Core wire sheath 1: Lead sheath.
Core wire sheath 2: PE sheath.
Padding layer: Padding layer.
Armor: Galvanized steel wire filled with asphalt material.
Outer sheath: Polypropylene fiber.
Electrical data
127/220(245) kV
| Nominal cross-sectional area | capacitance | inductance | Charging current per phase @ 50Hz |
| mm² | μF/km | mH/km | A/km |
| 500 | 0.14 | 1.42 | 5.8 |
| 630 | 0.16 | 1.40 | 6.4 |
| 800 | 0.17 | 1.37 | 6.9 |
| 1000 | 0.19 | 1.35 | 7.4 |
| 1200 | 0.20 | 1.33 | 7.8 |
| 1400 | 0.21 | 1.32 | 8.2 |
| 1600 | 0.22 | 1.31 | 8.6 |
160/275(300) kV
| Nominal cross-sectional area | capacitance | inductance | Charging current per phase @ 50Hz |
| mm² | μF/km | mH/km | A/km |
| 500 | 0.14 | 1.42 | 6.8 |
| 630 | 0.16 | 1.40 | 7.7 |
| 800 | 0.17 | 1.37 | 8.3 |
| 1000 | 0.18 | 1.35 | 9.0 |
| 1200 | 0.19 | 1.33 | 9.5 |
| 1400 | 0.20 | 1.32 | 10.0 |
| 1600 | 0.21 | 1.31 | 10.4 |
200/345(362) kV
| Nominal cross-sectional area | capacitance | inductance | Charging current per phase @ 50Hz |
| mm² | μF/km | mH/km | A/km |
| 630 | 0.14 | 1.40 | 8.8 |
| 800 | 0.15 | 1.37 | 9.7 |
| 1000 | 0.17 | 1.35 | 10.7 |
| 1200 | 0.18 | 1.33 | 11.1 |
| 1400 | 0.19 | 1.32 | 11.6 |
| 1600 | 0.20 | 1.31 | 12.1 |
230/400(420) kV
| Nominal cross-sectional area | capacitance | inductance | Charging current per phase @ 50Hz |
| mm² | μF/km | mH/km | A/km |
| 630 | 0.13 | 1.40 | 9.6 |
| 800 | 0.15 | 1.37 | 10.7 |
| 1000 | 0.16 | 1.35 | 11.7 |
| 1200 | 0.18 | 1.33 | 12.9 |
| 1400 | 0.19 | 1.32 | 13.5 |
| 1600 | 0.19 | 1.31 | 14.1 |
Size and weight
127/220(245) kV
| Nominal cross-sectional area | nominal conductor diameter | Nominal insulation thickness | Nominal insulation outer diameter | Nominal lead sheath thickness | nominal outer diameter | weight |
| mm² | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/m |
| 500 | 26.2 | 24.0 | 77.6 | 2.9 | 111.0 | 29.3 |
| 630 | 29.8 | 23.0 | 79.2 | 3.0 | 112.8 | 31.2 |
| 800 | 33.7 | 23.0 | 83.1 | 3.1 | 117.5 | 34.5 |
| 1000 | 37.9 | 23.0 | 87.3 | 3.1 | 121.9 | 37.7 |
| 1200 | 41.2 | 23.0 | 90.6 | 3.1 | 125.2 | 40.4 |
| 1400 | 44.4 | 23.0 | 93.8 | 3.1 | 128.6 | 43.2 |
| 1600 | 47.4 | 23.0 | 96.8 | 3.1 | 131.8 | 46.0 |
160/275(300) kV
| Nominal cross-sectional area | nominal conductor diameter | Nominal insulation thickness | Nominal insulation outer diameter | Nominal lead sheath thickness | nominal outer diameter | weight |
| mm² | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/m |
| 500 | 26.2 | 26.0 | 81.6 | 3.0 | 115.2 | 31.1 |
| 630 | 29.8 | 24.0 | 81.2 | 3.0 | 114.8 | 31.8 |
| 800 | 33.7 | 24.0 | 85.1 | 3.1 | 119.5 | 35.2 |
| 1000 | 37.9 | 24.0 | 89.3 | 3.1 | 123.9 | 38.4 |
| 1200 | 41.2 | 24.0 | 92.6 | 3.1 | 127.4 | 41.6 |
| 1400 | 44.4 | 24.0 | 95.8 | 3.1 | 130.6 | 44.4 |
| 1600 | 47.4 | 24.0 | 98.8 | 3.1 | 133.8 | 47.2 |
200/345(362) kV
| Nominal cross-sectional area | nominal conductor diameter | Nominal insulation thickness | Nominal insulation outer diameter | Nominal lead sheath thickness | nominal outer diameter | weight |
| mm² | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/m |
| 630 | 29.8 | 28.0 | 89.2 | 3.1 | 123.4 | 35.2 |
| 800 | 33.7 | 27.0 | 91.1 | 3.1 | 125.9 | 37.5 |
| 1000 | 37.9 | 26.0 | 93.3 | 3.1 | 128.1 | 39.9 |
| 1200 | 41.2 | 25.0 | 94.6 | 3.1 | 129.4 | 42.0 |
| 1400 | 44.4 | 25.0 | 97.8 | 3.1 | 132.8 | 44.9 |
| 1600 | 47.4 | 25.0 | 100.8 | 3.1 | 135.8 | 47.7 |
230/400(420) kV
| Nominal cross-sectional area | nominal conductor diameter | Nominal insulation thickness | Nominal insulation outer diameter | Nominal lead sheath thickness | nominal outer diameter | weight |
| mm² | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/m |
| 630 | 29.8 | 32.0 | 98.2 | 3.1 | 132.8 | 38.8 |
| 800 | 33.7 | 30.0 | 98.1 | 3.1 | 133.1 | 40.2 |
| 1000 | 37.9 | 29.0 | 100.3 | 3.1 | 135.3 | 42.6 |
| 1200 | 41.2 | 27.0 | 99.6 | 3.1 | 134.6 | 44.0 |
| 1400 | 44.4 | 27.0 | 102.8 | 3.1 | 138.0 | 46.9 |
| 1600 | 47.4 | 27.0 | 105.8 | 3.1 | 141.0 | 49.7 |
Before leaving the factory, every cable undergoes 24-hour power frequency withstand voltage, impulse voltage, bending cycle, and watertightness tests to ensure “zero defects before deployment.”
Beyond products, TST CABLE provides full lifecycle protection for power cables.
From route surveying, customized design of cables/sealing modules, and factory pre-fabricated terminations, to laying guidance, on-site testing, and operation and maintenance support, we provide a one-stop turnkey service. The TST CABLE professional team can respond to global emergency needs within 24 hours, ensuring your project runs smoothly without worries.
TST CABLE understands that the laying of every kilometer of submarine cable is not only an engineering feat but also a solemn commitment to a carbon-neutral future. When wind turbines rotate in the distant sea, and current flows through the deep blue, lighting up city lights, driving factory gears, and warming thousands of homes – behind it all is the energy link we have meticulously crafted.
By choosing TST CABLE high-voltage low-smoke halogen-free flame-retardant cables, you gain more than just a cable;
you gain a trust that transcends the deep sea and spans time.
Let clean power flow from the ocean to the future.
Also available in:
English





